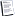 Adobe Audition 1.5 allows WMA monoaural audio at 44.1 KHz sample-rate with a bit-rate of 20 kbps
Adobe Audition 1.5 allows WMA monoaural audio at 44.1 KHz sample-rate with a bit-rate of 20 kbps
Hi:
Adobe Audition 1.5 allows WMA monaural audio at 44.1 KHz sample-rate
with a bit-rate of 20 kbps. How does it do this? How can the bit-rate
be less than the sample-rate?
In a monaural WMA file that is 44.1 KHz sample rate, what is the
minimum bit-rate that is mathematically-required? Can it be compressed
to 1-bit-per-second while still retaining the 44.1 KHz sample-rate? If
so, then how? If not, then why?
What version of WMA does Adobe Audition 1.5 use?
Also, why do WMA artifacts sound different from MP3 artifacts? What is
the mechanism behind WMA compression that gives WMA its characteristic
artifacts?
I like WMA-specific audio artifacts. All non-WMA digital audio
compressions that are below 320 kbps and/or below 44.1 KHz-sample-
rate, and/or non-monaural sound like stinky human fart. Or an angry
infant foaming at the mouth.
The only digital audio compression I like is WMA. The sounds resulting
from WMA compression sort of make me think of those RF electronic
telecommunication devices used in The Bourne Identity. That movie
features some really awesome devices that make those interesting
sounds - for example, when the main character is getting his hand
screened. I also associate these sounds with the electronic
telecommunication devices used by the Soviet Union. Soviet Union has
got some really psychedelic sounds in their electronics. You know,
those fancy dial-up modems tones?
All digital audio compression formats other than WMA, stink badly!!
Here are my rules for digital audio:
A. Whether compressed or not, the audio must be monaural and with a
sample-rate of at least 44.1 kHz.
B. The only compression allowed is WMA. No other compression format is
permitted.
C. In its uncompressed form, the audio must have a bit-resolution of
at least 16-bit
D. If compression is used, then the sample-rate of the compressed and
the uncompressed version of the audio must be the same.
E. If compression is used, the only thing that should be decreased is
the bit-resolution. The sample-rate must remain unchanged
Let's say a song that was originally recorded in stereo is given to
me. The song must to be converted to mono* via the following steps:
1. Record audio from CD [or other stereo audio source] into Wavelab,
Adobe Audition [or other audio software] into a file. For simplicity
let's call this file "Track1.wav"
2. Make a copy of Track1.wav and save the copy as "Track1B.wav"
3. Open Track1.wav and reduce the gain of its audio by 77.5%
4. Convert Track1.wav to monaural audio
5. Save Track.1
6. Open Track1B.wav and reduce its audio gain by 50%
7. Invert the phase of the left channel of Track1B.wav
8. Convert Track1B.wav to mono
9. Save Track1B.wav
10. Create a new stereo wave file whose bit-resolution is 16-bit and
sample rate is 44.1 kHz. For simplicity let's call this file
"untitled.wav"
11. Copy and paste the audio of Track1.wav into the left channel of
untitled.wav
12. Copy and paste the audio of Track1B.wave into the right channel of
untitled.wav
13. Convert untitled.wav to mono
14. Save untitled.wav
*Songs that were originally-recorded in stereo need to be converted to
mono via the above 14 steps because different sounds are recorded
differently in the L and R channels. The audio that is originally
panned to the center is significantly louder than the audio whose
phase is different in the left & right channels. This is why I reduce
the loudness of non-inverted stereo audio file by 77.5% [before
converting it to mono].
In the stereo file whose left channel has its phase inverted, I
decrease the loudness only by 50% and then convert it to mono. Usually
-- the lead vocals, bass, and percussion are recorded identically in
both the left and right channels. The piano, chorus, guitar, and synth
pads are usually recorded differently in the left and right channel.
|